Curved Mirror
Curved Mirror: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Radius of Curvature of Spherical Mirror, Principal Axis of a Spherical Mirror, 1/V versus 1/U Graph for Spherical Mirror & Derivation of Relation of Focal Length and Radius of Curvature of Spherical Mirrors etc.
Important Questions on Curved Mirror
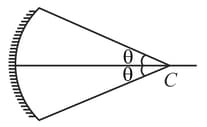
The circular boundary of the concave mirror subtends a cone of half angle at its centre of curvature. The minimum value of for which ray incident on this mirror parallel to the principle axis suffers reflection more than one is
A point source of light is 60 cm from a screen and is kept at the focus of a concave mirror which reflects light on the screen. The focal length of the mirror is 20 cm. The ratio of average intensities of the illumination on the screen when the mirror is present and when the mirror is removed is:
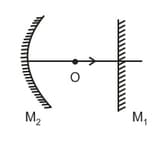
In the figure shown if the object 'O' moves towards the plane mirror, then the image I (which is formed after successive reflections from M1 & M2 respectively) will move:
A luminous point object is moving along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm towards it. When its distance from mirror is 20 cm its velocity is 4 cm/s. The velocity of the image in cm/s at that instant is:
An infinitely long rod lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length . The near end of the rod is at a distance from the mirror. Its image will have a length
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, it is found that there is no gap between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of the convex mirror is:
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be:

A large temple has a depression in one wall. On the floor plan, it appears as an indentation having a spherical shape of radius . A worshipper stands on the centreline of the depression, out from its deepest point, and whispers a prayer. Where is the sound concentrated after reflection from the black wall of the depression?
A thin road of length d/3 is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length = d such that its image, which is real and elongated, just touches the rod. Find the length of the image?
An object is placed at from the concave mirror of focal length the nature of the image and magnification will be
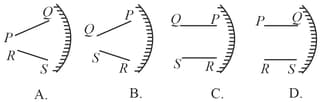
A person looks at the image of two parallel finite length lines and in a convex mirror (see figure)
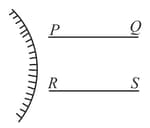
Which of the following represents schematically the image correctly? (Note : letters and are used only to denote the endpoints of the lines.)
In a concave mirror for real images magnification is taken in respect of heights.
The centre of a sphere of which the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is a part is called
Mirror having a curved reflecting surface are called as spherical mirrors.
Mirror having a curved reflecting surface are called as_____ mirrors.
